## Introduction to AI Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved over the past decade, leading to significant transformations across various industries. AI automation, which encompasses a range of technologies including AI agents, agentic workflows, and multimodal AI agents, is reshaping how businesses operate. This article explores these concepts, their definitions, applications, and the future developments we can expect in the realm of AI automation.
## Defining Key Concepts
### AI Automation
AI automation refers to the use of AI technologies to perform tasks that traditionally require human intervention. This includes automating repetitive tasks, enhancing decision-making processes, and improving efficiency across workflows.
### AI Agents
AI agents are software entities that can perform tasks on behalf of users by perceiving their environment and taking actions to achieve specific goals. These agents can operate independently or in collaboration with humans, adapting to changes in their environment.
### Agentic Workflows
Agentic workflows are structured processes where AI agents interact with other agents or systems to complete tasks. These workflows enable seamless integration of AI capabilities into existing business processes, enhancing productivity and reducing the time required to complete tasks.
### Full Work Automation
Full work automation aims to automate entire job functions or workflows, minimizing human involvement. This can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency gains, but it also raises questions about job displacement and the future of work.
### Auto-Works Platform
An Auto-Works platform is a comprehensive solution that integrates various AI tools and technologies to facilitate automation across different functions. These platforms often include features for managing workflows, monitoring performance, and optimizing processes.
### AI Voice Assistants
AI voice assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri, utilize natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to user commands. These assistants have become commonplace in consumer technology and are increasingly being adopted in business environments to streamline operations.
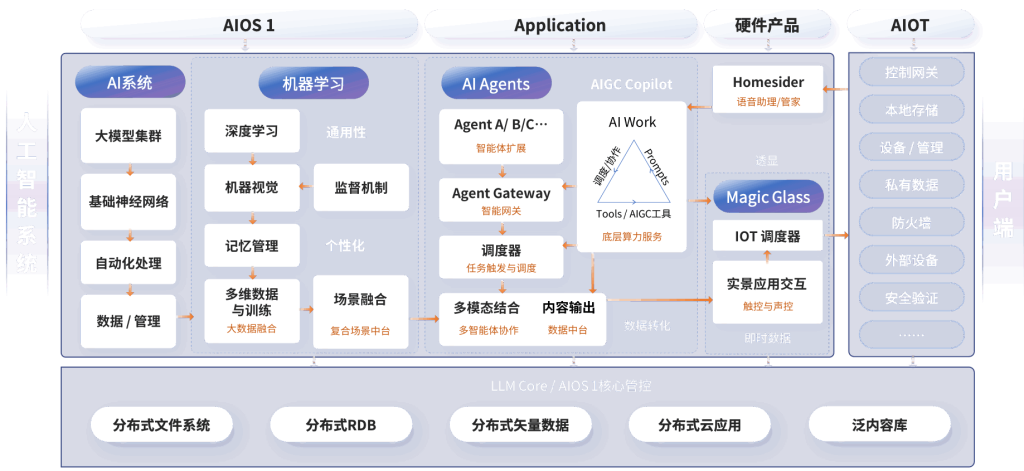
### AI Operating Systems (AIOS)
AIOS refers to platforms that provide the infrastructure for developing and deploying AI applications. These systems support various AI functionalities, including machine learning, data processing, and integration with other software tools.
### AI Large Models
AI large models, such as OpenAI’s GPT-3, leverage vast amounts of data and advanced algorithms to perform complex tasks like text generation, translation, and summarization. These models are at the forefront of AI research and development, enabling new applications across industries.
### Multimodal AI Agents
Multimodal AI agents can process and analyze data from multiple sources, such as text, audio, and images. This capability allows them to understand and interact with the world in a more human-like manner, making them valuable in applications ranging from customer service to autonomous driving.
## Current Trends in AI Automation
The development of AI automation technologies is being driven by several key trends:
1. **Integration of AI into Existing Systems**: Businesses are increasingly integrating AI tools into their existing workflows to enhance productivity and efficiency. This trend is evident in industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, where AI is used to automate routine tasks and improve decision-making.
2. **Advancements in Natural Language Processing**: The rise of AI voice assistants and chatbots has been fueled by advancements in NLP. These technologies are enabling more natural interactions between humans and machines, making it easier for businesses to implement AI solutions.
3. **Focus on Data Privacy and Intellectual Property Protection**: As AI technologies become more prevalent, concerns about data privacy and intellectual property protection are growing. Companies are investing in secure AI systems to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with regulations.
4. **Development of Autonomous Driving Simulation Environments**: The automotive industry is leveraging AI to develop autonomous driving technologies. Simulation environments allow engineers to test and refine AI algorithms in a controlled setting, accelerating the development of self-driving vehicles.
## Value of AI Automation
The value of AI automation is multifaceted. Businesses that adopt these technologies can expect to see:
– **Increased Efficiency**: Automating repetitive tasks allows employees to focus on higher-value work, leading to improved productivity.
– **Cost Savings**: Reducing the need for human intervention in routine tasks can significantly lower operational costs.
– **Enhanced Decision-Making**: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, providing insights that inform better business decisions.
– **Improved Customer Experience**: AI voice assistants and chatbots enhance customer interactions by providing quick and accurate responses to inquiries.
## Tools and Applications
Several tools and platforms are available to facilitate AI automation:
– **RPA (Robotic Process Automation)**: RPA tools automate rule-based tasks, such as data entry and processing. Companies like UiPath and Automation Anywhere are leaders in this space.
– **AI Development Frameworks**: Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch enable developers to build and deploy AI models efficiently.
– **AI-Powered Analytics**: Tools like Tableau and Power BI leverage AI to provide advanced analytics capabilities, helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
### Industry-Specific Use Cases
1. **Healthcare**: AI automation is transforming healthcare through applications such as predictive analytics for patient outcomes, automated scheduling, and AI-driven diagnostics.
2. **Finance**: In finance, AI is used for fraud detection, risk assessment, and automated trading, enhancing operational efficiency and security.
3. **Manufacturing**: AI-driven robots and automation systems streamline production processes, reduce downtime, and improve quality control.
4. **Retail**: Retailers are using AI for inventory management, personalized marketing, and customer service, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
## Future Developments
The future of AI automation is promising, with several developments on the horizon:
– **Greater Integration of AI and IoT**: The convergence of AI and the Internet of Things (IoT) will lead to smarter systems that can autonomously manage resources and optimize operations.
– **Advancements in Multimodal AI**: Future AI agents will be able to process and analyze data from various modalities, leading to more sophisticated applications in areas like customer service and autonomous systems.
– **Ethical AI Development**: As AI technologies become more integrated into society, there will be a growing emphasis on ethical AI development, focusing on fairness, accountability, and transparency.
– **Continued Growth of AI Large Models**: The development of larger and more capable AI models will enable new applications and improve existing ones, driving further innovation across industries.
## Conclusion
AI automation, encompassing a range of technologies and methodologies, is fundamentally transforming how businesses operate. From enhancing efficiency and decision-making to improving customer experiences, the impact of AI is profound. As we look to the future, the continued evolution of AI technologies will further reshape industries, creating new opportunities and challenges. Embracing these changes will be crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in an increasingly automated world.
### Sources
1. “The Future of Work: AI and Automation” – McKinsey & Company
2. “AI in Healthcare: Transforming the Future of Patient Care” – Deloitte Insights
3. “Robotic Process Automation: A Guide for Beginners” – UiPath
4. “The Role of AI in the Financial Services Industry” – PwC
5. “Multimodal AI: The Future of Intelligent Systems” – MIT Technology Review